Open-source 3-D printing Technologies
6 hours
Keywords
-
Additive manufcturing
-
Digital fabrication
-
Open source 3D printer
Learning Objectives
- Benefit from the Digital Fabrication
- Use open digital technologies to create, manipulate, prepare and publish 3D content
- Use open digital technologies to find and take advantage of 3D model repository
Materials
- Personal computer
- Internet connexion
- Tinkercard
- Scketchfab
Introduction
Significant advances in additive manufacturing (AM) technologies, commonly known as 3D printing, over the past decade have trans-formed the ways in which products are designed, developed, manufac-tured, and distributed.
3D printing’s ability and advantages over traditional manufacturing open plenty of opportunities for verticals, spanning from product design and development, customization service, to restructuring of supply chain for higher efficiency. European Commission, The disruptive nature of 3D printing
The introduction of additive manufacturing (AM), better known as 3D printing, emerges as a disruptive technology that brings with it several changes and impacts to the traditional product. A growing number of companies and new business models based on AM are emerging, cre-ating great opportunities for the economy and society. After providing students with a basic background of AM, digital fabrica-tion and Open Source 3D Printing (1st session), the Course will involve an intensive learning of open source hardware and software and open source platforms for creation of 3D objects.
The sessions will allow learners to acquire some technical skills needed to take full advantage of all the opportunities offered by 3D technologies. Participants will experience the design process by designing an object using Open-source 3-D printing technologies.
Context
3D printers are fast becoming a widely used manufacturing device which has revolutionised the manufacturing industry. The purpose of this training course is to introduce participants to AM and the most powerful benefits of the 3D Printing Technologies and the use of open digital technologies. At the end of the sessions, participants will be able to create 3D objects using open digital technologies, sharing their own projects and using other user’s projects.
Sessions
First session: Digital transformation in manufacturing "Additive Manufacturing" (AM)
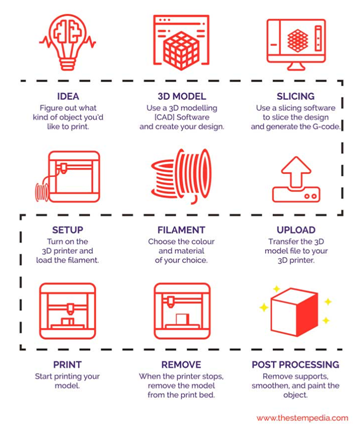
In recent decades, communications, imaging, architecture and engineering have all undergone their own digital revolutions. The term “digital transformation” refers to the use of digital data, connectivity, and processing encompasses every aspect of manufacturing activity. AM provides us with an opportunity to completely rethink the way products find their way to the end user. The session aims to provide learners with a broad overview of design and digital fabrication, introducing learners to the 3D printing, how it works and how it can be used in various industries. Students will learn what 3D Printing is, how 3D Printers work, and the types of objects you can make using this technology.
Second session: Let’s explore open digital technologies to design, develop, customize and share 3D products
The future of manufacturing is digital. 3D printers are fast becoming a widely used manufacturing device which has revolutionised the manufacturing industry. In 3D Printing Work, all starts with a 3D model. The session aims at introducing open source software and platforms for designing and sharing 3D contents. Students will experience the design process by designing/finding 3D objects using Tinkercad (platform to publish, share, and discover 3D content on web, mobile, AR, and VRI) and Sketchfab (tool for publishing and finding 3D Models online). Participants will acquire the technical skills to get started in AM needed to take full advantage of all the opportunities offered by 3D technologies.
Presentation
-
Digital transformation in manufacturing "Additive Manufacturing" (AM)
150 min
Learning Objectives
- Identify the key features and benefits of AM
- Discover how 3D Printers work and the types of objects users can make using this technology
- Explore the potential of AM as a tool for addressing the Digital Transformation challenges
Group discussion
Trainer will start the introduction to the module by asking participants about their previous knowledge/experience in the field of digital fabrication. Participants will focus on the pros and cons of digital fabrication. Answers will be documented and then reused to customize the training material.
“What is Additive Manufacturing?”
The history of digital fabrication - from hand production to 3D Printing. All began with the industrial revolution. Workers transitioned from hand production to new methods carried out with the help of machines. Digital fabrication is a type of manufacturing process where the machine used is controlled by a computer. The term Digital Manufacturing has somewhat of a broad meaning that could describe many parts of today’s modern manufacturing process. This industry is complex and there are many modern fabrication techniques, the most common forms of digital fabrication are:
- CNC Machining: shapes are cut out of wooden sheets.
- 3D Printing: objects are built up out of layers of metal or plastic.
- Laser Cutting: materials like metal are burnt or melted by a laser beam.
AM also known as 3D printing, is a process that creates a physical object from a digital design. AM printing enables users to produce complex shapes using less material than traditional manufacturing methods. But how Does 3D Printing Work? It all starts with a 3D model. There are many different 3D modeling open source software (e.g.Tinkercad, Skecthfab) for creating a 3D model or download it from a 3D repository.
“What You Get – The benefits of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing”
Additive manufacturing allows the creation of lighter, more complex designs that are too difficult or too expensive to build using traditional dies, molds, milling and machining. AM encompasses many forms of technologies and materials as 3D printing is being used in almost all industries we could think of. From fashion to car manufacturing, 3D printing is changing the way the world designs, creates, and engineers products.
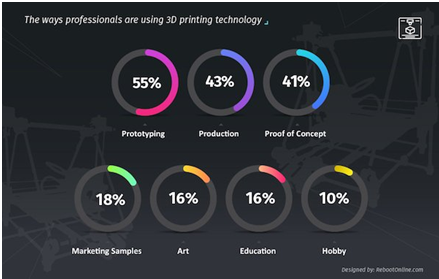
“The industry outlook for 3D printing will potentially have a greater impact on the world over the next 20 years than all of the innovations from the industrial revolution combined,” according to Deloitte. Digital fabrication comes with a range of benefits – some obvious and some less intuitive, from rapid response, reduced lead times, rapid manufacturing and use of unique materials and economies of scale. AM application is limitless, it should be seen as a cluster of diverse industries with a myriad of different applications. The following are some of the industries that are set to be transformed by 3D printing; construction, automobile, fashion, healthcare, culture (e.g. museum) etc.
Homework
Participants should watch some video about AM and take notes while they watch the videos:
- 3D Printing and Digital Fabrication.
- Digital fabrication, a tale of two worlds: Christian Weichel at TEDxLancasterU.
References
-
Let’s explore open digital technologies to design, customize and share 3D products
360 min
Learning Objectives
- Explore 3D printing software settings
- Recognize the principles of designing models for 3D printing
- Produce models and prototypes
- Use open digital technologies to design, publish, share, and discover 3D content
- Encourage the sharing and reuse of 3D content
- Explore the potential of the open digital technologies as a tool for addressing the Digital Transformation challenges
- Benefit from collaborative programming environment
Introduction
Group discussion on open digital technologies to design and share 3D content Trainer will start the introduction to the module by asking participants about their 3D modelling experience.
Design, create and invent with new media: what one actually learns from 3D printing?
Presentation and analysis of the benefits of 3D printing. Considering that hat digital fabrication is the merging of the human with the technical, the result is a creative product formed from their ideas and executed through a series of complex design decisions. So, through 3D design and making, users have the opportunity to develop multiple skills, not only professional (proficiency in 3D) , but also in spatial development and a variety of mathematical concepts as well as personal ones.
In fact, the use of digital fabrication technologies promotes curiosity-driven, self-directed, creative learning. It supports users to think creatively, reason systematically– essential skills for life in the 21st century.
The 3D design software Tinkercad
Tinkercad is a free and easy to use 3D design software that helps 3D starters all over the world think, create and make. Tinkercad was founded as a company in 2010 in the European Union by Kai Backman and his cofounder Mikko Mononen, with a goal to make 3D modeling, especially the design of physical items, accessible to the general public, and allow users to publish their designs under a Creative Commons license.
Since it became available, it has become a popular platform for creating models for 3D modeling and printing. Tinkercad uses a simplified constructive solid geometry method of constructing models. A design is made up of primitive shapes that are either "solid" or "hole". Combining solids and holes together, new shapes can be created, which in turn can be assigned the property of solid or hole. Shapes can be imported in three formats: STL and OBJ for 3D, and 2-dimensional SVG shapes for extruding into 3D shapes. Tinkercad exports models in STL or OBJ formats, ready for 3D printing.
3D starters can learn the basics of creating digital 3D models that could be printed on a 3D printer. Users can work their way through several tutorials to learn the basics of the program for creating and sharing their Tinkercad Projects.
Sketchfab: the importance of the collaborative programming environment
Sketchfab is the world's largest platform to publish, share, and discover 3D content on web, mobile, AR, and VR. Such open digital technology plays a key role in empowering a new era of creativity by making it easy for anyone to publish and find 3D content online. Being the largest platform for immersive and interactive 3D, Sketchfab allows users to share their 3D work showcasing their skills, as well as share and embed 3D models anywhere online.
Homework
TINKERCAD
- Login to your Tinkercad account and, following the instructions make a ring using cylinder shapes. After designing a 3D basic ring, you are now ready to design a pair of glasses.
SKETCHFAB
- Upload your 3D Model to your Sketchfab profile.
Go to this model page and click Download under the viewer to download the FBX file available. Once you have a 3D model ready, it’s time to upload. Login to your Sketchfab account.
- Check the Appearance.
Once the model is done uploading, users can take advantage of a number of Sketchfab tools to make it look even better.
- 3DSetting.
Using the Scene tab, can change your model's orientation by 90° increments around the x-, y-, or z-axis, or you can fine-tune it by selecting “Show advanced rotation”.
- And now... publish and share your 3D Model!
It is now time to publish your 3D Model so people can see and use it! Under Manage Your Model) you can to make your 3D model visible online and downloadable. Then, show off your model on your social media.
References